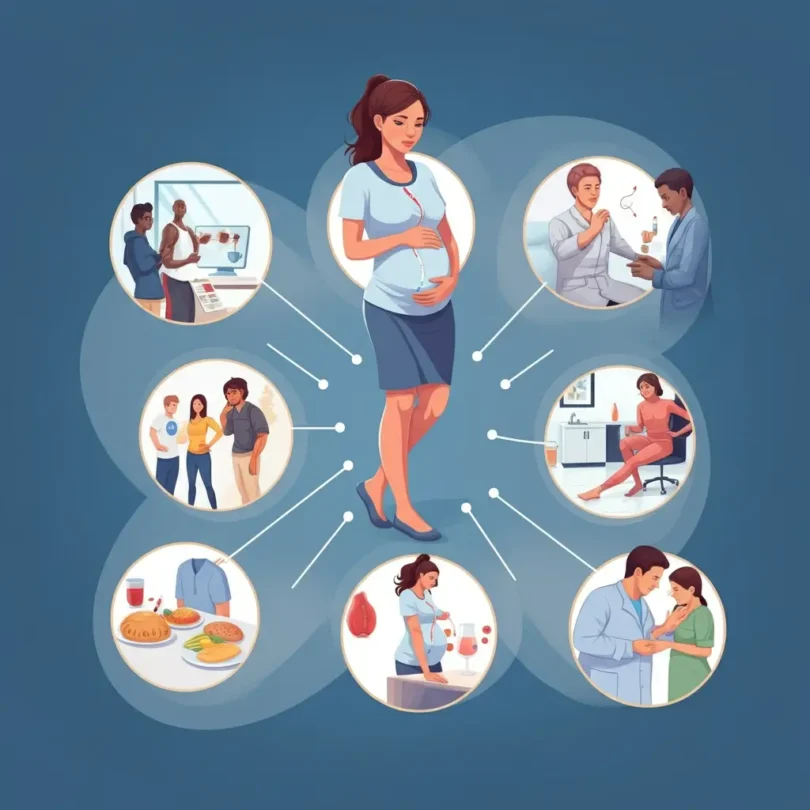
Gestational Diabetes Treatment
The aims Gestational Diabetes treatment is to decrease the blood glucose levels and the risk for an increased birth weight and complications. After eight hours of fasting, the blood sugar levels should be below 95 mg / dl. Two hours after eating the blood sugar levels should not be higher than 120 mg / dl. For most affected pregnant women, the normal blood sugar levels can be achieved with the help of proper nutrition. If this is insufficient, than insulin is used to normalize the blood glucose level. The oral hypoglycemic agents (metformin, sulphonylureas, etc.) are so far not approved to use during pregnancy.
Dietary Recommendations
Most of the gestational diabetes can cure through sufficient nutrition therapy. The recommended amount of energy should be 1800-2000 kilo calories (kcal) per day.
Nutrition have important role in control of type 4 diabetes so patient must pay attention to his diet, healthy diet is sign of healthy life.
- Select a possible low-carb breakfast, since in the morning, the blood glucose levels are usually higher than the day time due to increased insulin resistance . Examples:
- Dairy products such as yogurt or cottage cheese with fruit
- Eggs (omelets, scrambled eggs, boiled egg, …)
- if cereals, then, for example, whole meal bread with cheese, salmon, ham
- Distribute the caloric value evenly on the meal plan.
- Eat plenty of vegetables, fruit and fiber in moderation.
- Eat several small meals rather than fewer large (4-5 smaller meals a day).
- Use low-fat dairy and meat products.
Drugs Therapy For Gestational
If blood sugar level cannot be normalized by changing diet and physical activities, than drug therapy with insulin is may be necessary. In most cases, small amounts of short-acting insulin are used before meals to prevent excessive blood sugar levels. The insulin is injected under the skin (subcutaneously).
Sometimes additionally a long-acting insulin is injected in morning after getting up and in the evening before bedtime, , which covers the basic needs of this hormone and can be supplemented with short-acting insulin doses before meals. Particularly comprehensive training is necessary for pregnant women, so that the correct dose of insulin is selected and injected on correct time. Too high dose of insulin may cause hypoglycemia and have serious consequences for both mother and child.
Anti-diabetic drugs in the foam of tablet (oral anti-diabetics) cannot be taken during pregnancy diabetes. It is not yet clarified that whether what type of harms these drugs causing during pregnancy. In some countries the drug Met-formin is also approved for pregnant women, if the blood sugar levels cannot be sufficiently lowered with the help of insulin.