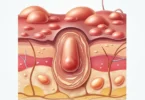
A malignant melanoma or black skin cancer is an aggressive, highly malignant skin tumor that occurs predominantly on areas of the skin that expose to sunlight (e.g. face, neck, arms and lower legs). A malignant melanoma occurs not only on expose parts of the body, but also on other part of skin. In men, skin cancer mainly occur on the trunk (for example on the back), in women mainly forms on arms and legs. Skin cancer may also develop in “hidden parts of the body” such as the feet, the genital area, the scalp or the skin underneath a nail. Fair-skinned people with weak browning tendency are more likely to develop melanoma. Compared to other types of skin cancer, the black skin cancer spreads relatively early to other organs (metastasis).
The term melanoma indicates that black skin cancer arises from the pigment cells so-called melanocytes, which are responsible for skin color. Melanocytes are located in the epidermis (epidermis) and contain the pigment substance melanin.
Black skin cancer can grow both in horizontal and in vertical direction. Through the horizontal growth melanoma skin absorbs visible in size. When it grows in vertical direction, it penetrates the blood and lymph vessels of the epidermis. Through theses infested blood vessels and lymph vessels cancer cells spread throughout the body and settle in other organs and multiply there. Basically, skin cancer through these secondary tumors infects any organ (metastasis).
Types of Melanoma
Black skin cancer occurs in various forms. The main types of melanoma are:
- Superficially spreading melanoma (SSM): Superficial spreading malignant melanoma has received its name from the fact that the tumor cells spread relatively long on the skin surface (Superficial spread well) before the tumor grows into the depths. Superficial spreading malignant melanoma is the most common type of malignant melanoma in Central Europe with about 60 percent of cases. The mean age of onset is 50 years. This common form of skin cancer forms flat irregularly shaped black, gray, blue, brown to white colored flock on the surface of the skin. Sometimes such melanomas take years to evolved from a nodular lesion, which then have a slight edge bead and tends to grow in height.
- Gnarled or nodular Melanoma (NM): Under a nodular melanoma is defined as a melanoma, that outset growth in the form of a significantly raised node. The average age of onset is 55 years. Approximately 20 percent of melanomas which occur in Central Europe belong to the type of nodular malignant melanoma. Compared to superficial spreading malignant melanoma it usually grows more rapidly into deeper layer of skin. A nodular malignant melanoma bulging hemispherical on the skin surface, and is gray-brown to reddish-blue black in color.
- Lentigo maligna melanoma (LMM): The lentigo maligna melanoma develops from a specific cancer precursor, which is called lentigo maligna (maligna = malignant lentigo = lenticular spot). Approximately 10 percent of malignant melanoma which occur in Europe are lentigo maligna melanoma. Such skin cancer occurs particularly in the elderly on the face. The lentigo maligna is usually appear as fuzzy, gray-brown to black and irregular in shape
- Acral lentiginous melanoma: In the Central Europeans acral lentiginous malignant melanoma accounts for only about 5 percent of all melanomas. The average age at onset is 65 years. Acral lentiginous malignant melanoma occurs at the palms and soles and nail area. In the early stages it forms brown to brownish black spots that may later ooze and bleed.
There are also rare species of malignant melanoma, which make up a total of about ten per cent of cases. To do this one:
- Amelanotic melanoma (that is not colored and is therefore very hard to detect it)
- vaginal melanoma
- Uveal melanoma
- Rectum melanoma
Causes of Melanoma
Symptoms of Melanoma
Diagnosis of Melanoma
Treatments of Melanoma
Preventions
You can prevent melanoma by avoiding external risk factors. Especially for very fair-skinned people, it is highly recommended to avoid intensive UV radiation . This applies both to natural UV radiation as well as artificial ( Solarium ).
To prevent skin cancer, it is important to:
- Avoid sunlight, especially in summer during the period from afternoon to evening.
- If you are in the sun, always protect yourself with sufficient sunscreens, light-proof fabrics, a hat and a UV-attenuating sunglasses .This is especially true for children.
Note
In case of any suspicious signs must visits your dermatologist because chance of cure is maximum if cancer is detected at an early stage.