Type A syndrome
The insulin resistance syndrome type A belongs to the group of extreme insulin-resistant syndromes (together with Leprechaunism, the Lipodystrophies, the Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome and the insulin resistance syndrome type B).
Symptoms of Type A Syndrome
It is characterized by the symptoms triad with
- Hyperinsulinemia
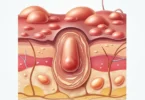
- Acanthosis nigricans (skin lesion with insulin resistance),
- Hyperandrogenism in women without Lipodystrophy and who are not overweight.
The syndrome is rare, It is generally diagnosed in young women with marked signs of hyperandrogenism, while nigricans acanthosis lead men and boys .
Causes of Type A Syndrome
- Occasional symptoms are a akromegaloides face and muscle spasms.
- Hyperinsulinemia is due to insulin resistance- a condition in which body develop resistance against insulin.
- Hyperandrogenism associated with the polycystic ovary syndrome or with ovarian Hyperthekose and causes impairment of fertility.
- In some cases, heterozygous mutations in the insulin receptor gene (INSR; 19p13.3-P13.2) is also cause of the syndrome. These mutations are located in the tyrosine kinase domain of the receptor, the inheritance is autosomal dominant.
- It is also been reported in patients with homozygous mutations in the insulin-binding domain of the receptor.
- Only 15-20% of female patients with Hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans have mutations in INSR gen.
The types A and B of the insulin resistance syndrome are distinguished by the absence of anti-insulin receptor autoantibodies in type A.
Treatments of Type A syndrome
Insulin resistance diabetes patients are treated nutritionally by giving balance diet and / or treated with medication (metformin, glitazones, or other antidiabetic agents).
Prevention
- Diagnose diseases which are responsible for causing Type A Syndrome
- If you find any sign or symptom of such diseases, contact with your physician for accurate treatments.