Malignant melanoma have best chance of cure if it is detected at an early stage. The disease can be cured if the tumor is still thin and has not penetrated into deeper layers of the skin (More than 97% cure rate in the early stages). Deeper the tumor cells penetrate in the dermis, the higher is the risk that these cells travel through the lymphatic and / or blood system in other parts of the body, where they lead to the occurrence of metastases. Then, the disease is poorly mastered.
Therefore, a regular self-examination is of great importance. If you notice any changes on the skin or on a liver spots, you should immediately show this to your dermatologist. This is especially true for high-risk patients. Even patients who have undergone surgery of melanoma need lot of care because they have an increased risk of developing a second melanoma. Relatives of melanoma patients should perform this self-examination regularly. ABCDE guide line helps us in self-examination.
In clinical diagnosis, first step is the physical examination of the skin in which the doctor use a magnifying glass to see the abnormal changes on a skin (dermatoscopy). These Dermatoscopes is an oily solution between the skin surface and the microscope optics, which prevents annoying reflections and the skin layers makes translucent. An experienced examiner recognize 90% of melanomas in this way more.
In further investigations ultrasound examination of the skin tumor or local lymph nodes are also performed. In addition to these, it is essential to remove the tissues from affected site (biopsy) and to investigate it histological for the exclusion of possible metastases. Only then a definitive statement to the diagnosis can be made.
Biopsy
In this step a sample of tissue is removed from the suspicious area of skin. This procedure is called biopsy and can be carried out in two different ways:
Excisional biopsy
The excisional biopsy is the preferred form for suspected melanoma. It includes the complete removal of the suspicious lesion, including a 1-3 millimeters of safety margin to the surrounding tissue. In general, the excisional biopsy can be performed under local anesthesia.
Incisional biopsy
In an incisional biopsy, first only a part of the suspicious lesion is removed. It is applied on those lesions which are very large or in those which are parts of the body such as the face, the palms or soles. On such cosmetically or functionally important sites, the diagnosis should be confirmed before the entire area of skin is removed.
This tissue sample is then examined histologically in a laboratory by a pathologist.
Pathological examination
The histological examination of the excised tissue in the laboratory currently offers the safest method to distinguish between a benign and a malignant lesion. Micro staging is crucial for determination of suitable treatment.
In Microsplitting Staging the following factors will be examined and evaluated:
- Type of melanoma
- tumor thickness
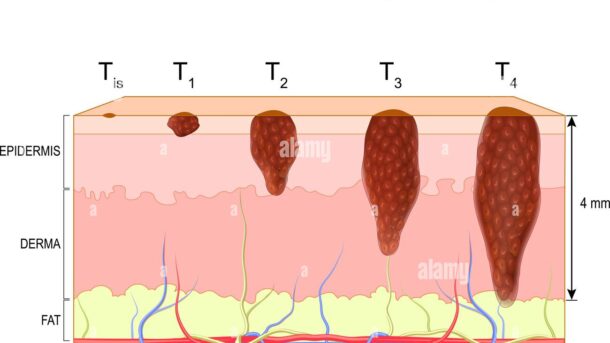
- Invasion degree (how deep the melanoma has already grown into the lower layers of the skin?)
- Ulceration (If the tumor has already broken through the top layer of skin? This change is not visible to the naked eye in some cases.)
The results of this study are the basis for an initial evaluation of the stage in which the malignant melanoma is present. In the early stages a cure is often possible by complete surgical removal of the tumor.
Special X-ray and blood tests will be done to detect any metastases in the body. Based on these and other criteria first statements on the risk of metastasis and prognosis (assessment of disease progression) can be taken.
A biopsy of the sentinel lymph node is also recommended if the melanoma is injected more than one millimeter deep into the skin.