Gestational Diabetes Or Type 4 Diabetes
The Type 4 Diabetes or Gestational Diabetes (GDM) is a very common condition that occurs in approximately 3.7 percent of pregnant women. As a rule, he is largely asymptomatic, however, the disease can lead to complications for mother and child. The elevated blood glucose levels can often be reduced only by adjusting the diet.
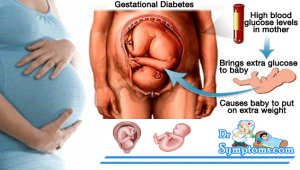
In order to supply the fetus with enough glucose, the mother’s body speaks naturally less well to insulin from the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. This has the consequence that the concentration of glucose in the blood increases. Women with gestational diabetes may not adequately distribute insulin to lower blood sugar in compensation. Due to the increased nutrient supply, the child is gaining weight, and have more common birth complications. The treatment of gestational diabetes include a change in diet, physical activity and in some cases, insulin therapy.
Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
In most cases, gestational diabetes is largely asymptomatic. The typical symptoms of diabetes such as excessive thirst (polydipsia), frequent urination (polyuria), fatigue and weakness are often very mild pronounced and to be interpreted differently in the context of pregnancy.
The consequences are often more serious for unborn child than the mother.The negative effects of sugar on the vessels leading to reduced blood flow to the placenta, which endangers the nutrition of the fetus (placental insufficiency). This problem is exacerbated by the mechanical pressure that could result from hydramnios. But gestational diabetes can indicate the following other symptoms:
- Frequent urinary, tract infections and vaginal thrush: The sugar in the urine has good conditions for bacteria and fungi propagation.
- Increased amount of amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios) may be determined by the gynecologist in the ultrasound.
- Excessive weight and the unborn child with increased size (macrosomia): The children of mothers with gestational diabetes often have a birth weight of more than 4500 grams.
- Hypertension (Hypertension): often occurs together with a gestational diabetes.
Causes Of Gestational Diabetes
According to current knowledge, the release of various hormones during pregnancy is primarily responsible for causing gestational diabetes. In addition, certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing a gestational diabetes.
The hormonal changes especially occur in the second half of pregnancy. In this pregnancy of the body produces large quantities of the hormones like
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
- Cortisol
- Placental lactogen
- Prolactin
For more information click here Causes of Gestational Diabetes.
Treatment of Gestational Diabetes
The treatments of gestational diabetes is based on two pillars, the change in diet and insulin adjustment. In 85% of cases, patients meet the dietary measures to optimize blood sugar and the remaining 15% will need additional insulin.
For more information about Treatments click Treatment of Gestational Diabetes
Precaution For Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes can be prevented by preventing
- Obesity
- Poor diet
- Any type of sugar, such as sweets, chocolate, glucose or sugary drinks.