Actinic Keratosis Or Solar Keratosis
The actinic keratosis is a specific lesion that produced by ultraviolet rays ( actinic means caused by radiation and keratosis means growth of keration on mucus membrane or on skin ). Since ultraviolet light occurs naturally in sunlight, actinic keratosis is also known as solar keratosis . The actinic keratosis is a skin condition that can develop into squamous cell carcinoma (squamous).
Dermatologists also consider actinic keratosis as in-situ carcinoma. Actinic keratosis is understood as an early form of skin cancer that can remain inconspicuous for long years. However, there is also the possibility that cancer cells spread in deeper layers of the skin (invasive squamous cell). Accordingly, the actinic keratosis by definition is considered as pre-cancer or even as early stage of squamous and therefore it is also called actinic pre-cancer .
the actinic keratosis is mainly produced in the body that are exposed to uv radiation from the sun. Actinic keratoses are relatively frequent: affects mostly fair-skinned people from the age of 50 with the skin type i or ii men are affected slightly more often than women.
Actinic Keratosis: Frequency
The actinic keratosis comes with great frequency in fair-skinned people. In countries with high uv radiation corresponding number of inhabitants are affected: in australia , about half of all light-skinned men between age of 30 and 70 has an actinic keratosis and in case of women about any third parties is affected.in the uk 15 percent of men and 6 percent of women have an actinic keratosis.
In up to 10 percent of cases, the actinic keratosis become a spinaliom. Who taking medication that suppress the immune system ( eg after an organ transplant ), has an even higher risk of skin cancer.
Actinic Keratosis: Causes
Since the risk for actinic keratosis increases with the number of cases in which the skin is exposed to strong uv radiation, the skin lesion develops frequently in the elder (called senile keratosis). However, the actinic keratosis occurs increasingly in younger people to.
In addition to age other important risk factors are:
- Living in areas with high uv radiation (eg at high altitude)
- Mainly applied in liberal professions
- Frequent outdoors leisure activities
- Scandinavian
- Severe sunburns in childhood
- Hereditary diseases associated with an impaired dna repair system (eg the pigmentosum xeroderma or moonlight disease)
- A permanently impaired immune system (for example in humans, who take medications that suppress the immune system)
When the immune system is permanently impaired, there is also an increased risk that actinic keratosis pass in a spinaliom. Skin infections caused by human papillomavirus (hpv) facilitating the transition of actinic keratoses in squamous likewise.
Actinic Keratosis: Symptoms
The typical symptoms for actinic keratosis are superficial lesions in body portions that particularly often exposed to sunlight. These particular body portions are:
- The face
- Back of the hands
- Forehead,
- The head (with a bald or sparse hair)
- Fore-arms.
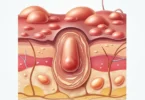
On a single or in several places it first comes as small redish spot that feels like fine sandpaper. They arise because the top layer of skin is thins. Blood vessels present under the top layer of skin is damaged by sunlight due to which this affected area become more prominent and appear as red (telangiectasia). Actinic keratosis causes no symptoms such as itching or burning, but may bleed more easily due to the increased vulnerability.
Later these spots develop into demarcated reddish nodules (papules), which are one half to one centimeter horny big and drab. The affected skin feels rough (similar to sandpaper).
Rarely actinic keratosis grows at a single site. Most lesions occur in small groups or distributed on large area (so-called multiple actinic keratoses ).
The actinic keratosis is considered as particularly skin cancer precursor because: the symptoms of the lesions are initially limited to the topmost cell layer of the skin (called epithelial tissue). It may spread into underlying tissue and proceed as a penetrating (invasive) tumor called spinaliom or squamous cell carcinoma. The transition to this form of non-melanoma skin cancer is fluent .
As important symptoms that associated with increased risk of transition of actinic keratosis in skin vare:
- Induration,
- Bleeding and
- Redness of the affected skin,
- A surface growth of actinic keratosis and
Even pain , excessive keratinization of the skin (hyperkeratosis) and itching may indicate that the actinic keratosis merges into a squamous.
Actinic Keratosis: Diagnosis
An actinic keratosis (solar keratosis) has a typical appearance, but cannot be reliably distinguish from other skin diseases by the naked eye. Such diseases are
- Age spots (solar lentigo)
- Common warts (verruca vulgaris),
- A fungal skin infection ( tinea )
- Eczema,
- The ordinary psoriasis (psoriasis vulgaris) or
- Malignant tumors such as squamous (squamous cell), the basal cell carcinoma (bcc) or lentigo maligna melanoma .
in order to safely detect the actinic keratosis and determine how pronounced it is, the doctor usually extracts a tissue sample from the affected skin and examined them under the microscope (so-called biopsy ). For smaller lesions he immediately removed the fabric often completely surgically and examined it then microscopically. A reliable diagnosis of actinic keratosis can be set only by such an investigation.
Actinic Keratosis: Therapy
The therapy depends on the location, size and extent. Also the patient’s age and other comorbidities influence the decision for the respective therapies for actinic keratosis. Treatment and aftercare are carried out by a dermatologist. The following treatment options are available:
- Surgical removal
- Freezing with liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy)
- Removal using a laser (eg, erbium yag laser)
- Removal with a sharp spoon or a ring curette (curettage)
- Applying caustic solutions (chemical peel)
- Local cytostatic therapy ( “chemotherapy in ointment form”, for example with 5-fluorouracil)
- Local application of an agent having an effect on the immune system (immune modulator such as imiquimod): the patient wears an imiquimod containing cream itself for several weeks on to the skin before bedtime.
- Photodynamic therapy (pdt): where a photo-sensitizer is administered as a drug, and subsequently activated by a laser.
- Diclofenac hyaluronic acid therapy
The laser therapy with carbon dioxide or erbium yag is mainly in single attached lesions. The possible side effects are blisters , pain , and possibly scarring or a local change in skin color or the treated areas may be locally ignite. In almost 100 percent of cases can be completely remove actinic keratosis with the laser.
A chemical peel is not quite as effective as a rule: the actinic keratosis is only reduced by this treatment mostly. The side effects of chemical peels are similar to those of the laser treatment; in addition, the skin may flake. After peeling a careful sunscreen is recommended.
Actinic Keratosis: Prognosis
The prognosis of actinic keratosis (solar keratosis) is generally good, if it is treated. In addition, an actinic keratosis is very slow to evolve.an actinic keratosis leads to complications when it passes into an expanding spinaliom in the further course. This happens in up to ten percent of cases within ten years. The spinaliom grows in the depth of the tissue, thereby destroying the adjacent structures and tends to form secondary tumors.
Actinic Keratosis: Prevention
An actinic keratosis is caused by uv radiation in the sun or tanning beds. Prevention is therefore simple: avoid too much natural or artificial uv radiation and protect your skin with sunscreen (high spf) and textiles. The uv radiation causes the skin to age faster and causes mutagenic of skin cells which result in actinic keratosis or skin cancer that’s way dermatologists warn of excessive and long sunbathing. Men with advanced balding develop particularly frequently actinic keratosis and should always wear a hat. Especially children should not expose to intensive sunlight since sunburns during childhood increase the risk of skin cancer.
For more information about cancer: